Food allergies and food sensitivities are often confused, but they are different conditions with distinct underlying mechanisms and symptoms. Understanding these dietary restrictions can help individuals manage their dietary needs effectively.
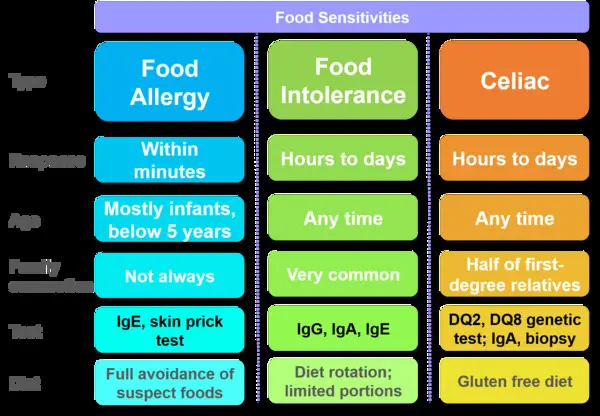
A food allergy is an immune system reaction that occurs shortly after consuming a particular food. It involves the production of immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies, which trigger the release of histamine and other chemicals. This can lead to symptoms such as hives, swelling, difficulty breathing and even anaphylaxis. This is a potentially life-threatening reaction and requires immediate medical attention with the use of an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen). Strict avoidance of the offending food is often necessary to manage dietary restrictions related to food allergies. Common food allergens include peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, fish, eggs, milk, wheat, soy as well as certain additives or preservatives.
Food Sensitivity
A food sensitivity or intolerance is a digestive system response rather than an immune system reaction. It typically involves the inability to properly digest or metabolize certain components of food, such as lactose (milk sugar) or gluten (a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye). Symptoms of food sensitivities may include bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal discomfort. They do not involve the immune system and are generally less severe than food allergies. Dietary restrictions for food sensitivities may involve eliminating or limiting certain foods or incorporating specific supplements.
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by the consumption of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. In people with celiac disease, the immune system attacks the small intestine when gluten is consumed, leading to inflammation and damage to the intestinal lining. This can cause a variety of symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, and nutrient deficiencies. Strict adherence to a gluten-free diet is the primary dietary restriction for individuals with celiac disease.
Testing for Dietary Restrictions
Testing for Dietary Restrictions: Food allergies are typically diagnosed through a combination of skin prick tests, blood tests (measuring IgE levels) and oral food challenges under medical supervision. These tests can identify specific allergens that trigger an immune response and help guide dietary restrictions.
Food insensitivities and intolerances are more challenging to diagnose. Often, an elimination diet or food challenge is introduced, where suspected foods are removed from the diet for a period of time and then reintroduced one by one to observe any reactions.
Lactose intolerance is a common food insensitivity caused by the lack of the enzyme lactase, which is responsible for breaking down lactose the sugar found in milk and diary products. People with lactose intolerance may experience symptoms such as bloating, gas and diarrhea after consuming dairy products. It is a type of food sensitivity and does not involve the immune system.
Managing Food Sensitivities
While food allergies are difficult to overcome and often require strict avoidance of the offending food. Yet, some food sensitivities or intolerance can be managed or potentially overcome through dietary modifications or supplementation. For example, individuals with lactose intolerance may be able to consume small amounts of dairy products or take lactase enzyme supplements to aid digestion.
Many diagnostic tests for food allergies and sensitivities are covered by insurance, but coverage may vary depending on the specific plan and the type of test ordered. Healthcare providers will typically specify which foods or allergens need to be tested based on the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and suspected triggers.
As always, all of the above is for information only and is not to be taken as medical advice. It is recommended to consult with a qualified healthcare professional, such as an allergist, gastroenterologist or nutritionist. They can order appropriate tests, interpret the results, and provide guidance on dietary modifications and management strategies.
By understanding and properly managing dietary restrictions related to food allergies and sensitivities, individuals can maintain their health and well-being while enjoying a diverse and balanced diet withing their specific dietary requirements.
Barry Schustermann
Follow me on X @BarrySchust
Follow me on Facebook @Barry Schustermann

1 thought on “Understanding Dietary Restrictions: Food Allergies and Sensitivities”