Diabetic cystopathy, a urological complication affecting individuals with long-standing diabetes, impacts bladder function and can significantly reduce quality of life. This condition occurs when prolonged high blood sugar levels damage the nerves controlling the urinary system. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
Contents
What is Diabetic Cystopathy
Diabetic cystopathy develops as a result of diabetic neuropathy, which disrupts normal bladder function. Patients may experience difficulty emptying their bladder completely, leading to various urinary issues. The signs of diabetic cystopathy often develops gradually, including decreased bladder sensation, infrequent urination, weak urine stream, and urinary retention.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Doctors diagnose diabetic cystopathy through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specialized tests. These may include urodynamic studies to assess bladder function and post-void residual volume measurements to check for incomplete bladder emptying. Early detection is key to preventing further complications and managing the condition effectively. LivWell Nutrition: Nourish Your Body & Well Being
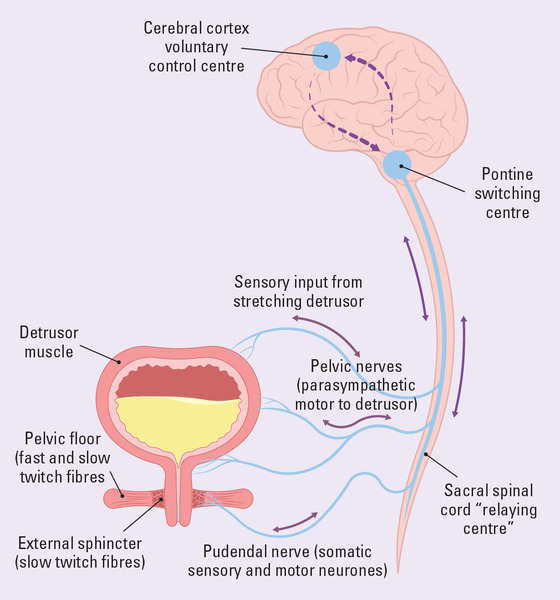
Pathophysiology of Bladder Disfunction
The development of diabetic cystopathy involves complex changes in the urinary system. Chronic hyperglycemia leads to oxidative stress and nerve damage, affecting both sensory and motor nerves in the bladder. This neuropathy impairs bladder sensation and contractility, resulting in poor bladder emptying and potential urinary tract infections. Micturition, the process of urinating, relies on coordination between the nervous system and bladder muscles. In diabetic cystopathy, this coordination is disrupted as bladder dysfunction may occur. Transform your Health with Ora Organic.
Complications and Associated Conditions
Diabetic cystopathy can lead to several complications, including recurrent urinary tract infections, bladder stones, kidney damage, and overflow incontinence. Additionally, it may coexist with other urological conditions, complicating diagnosis and treatment. Patients with diabetic cystopathy are also at higher risk of developing urge incontinence and stress incontinence due to the overall impact on bladder function.
Treatment Approaches
Managing diabetic cystopathy involves a multifaceted approach. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial to prevent further nerve damage. Implementing timed voiding schedules and pelvic floor exercise can improve bladder control. Medications can enhance bladder contractility, while others can reduce uretheral resistance. For patients with significant residual urine, intermittent catheterization may be necessary to ensure complete bladder emptying. In severe cases, advanced therapies like sacral neuromodulation may be considered. Learn more about Ritual Multi Vegan Supplements
Living with Diabetic Cystopathy
While diabetic cystopathy can significantly impact daily life, proper management can help patients maintain good quality of life. Patients should make lifestyle changes such as maintaining good hydration, practicing regular bladder emptying, and avoiding bladder irritants. Ongoing monitoring is essential, with regular check-ups allowing healthcare providers to assess bladder function, adjust treatments, and prevent complications. Education, adherence to treatment plans, and open communication with healthcare providers are key to successful management of this urological disorder.

Diabetic cystopathy is a complex condition requiring comprehensive care. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early, and following appropriate treatment plans, patients can effectively manage their bladder health. With ongoing research and advancements in treatment, the outlook for individuals with this bladder dysfunction continues to improve. As awareness grows, so does the potential for early intervention and improved outcomes in managing this challenging aspect of diabetes.
As always, all the information in this article is for information only, and is not to be taken as medical advice. Please see your medical doctor or health care provider for formal advise.
Barry Schustermann
Follow me on X @BarrySchust
Follow me on Facebook @Barry Schustermann
External References:
1. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) – Diabetic Neuropathy:
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-problems/nerve-damage-diabetic-neuropathies
2. American Diabetes Association – Bladder Issues:
https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/complications/neuropathy/autonomic-neuropathy/bladder-issues
3.Urology Care Foundation – Diabetes and Urologic Problems:
https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/d/diabetes-and-urologic-problems
4.International Diabetes Federation – Complications of Diabetes:
https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes/complications.html
5. Journal of Diabetes Research – Diabetic Bladder Dysfunction: Current Translational Knowledge:
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jdr/2018/1890978/


1 thought on “Diabetic Cystopathy: Understanding and Managing Bladder Dysfunction in Diabetes”
Comments are closed.