Psoriatic arthritis management is crucial for those living with this chronic inflammatory condition that affects both joints and skin. PsA is a complex disorder that can significantly impact daily life, but with proper treatment and care, individuals can maintain a good quality of life. Understanding the nuances of psoriatic arthritic and implementing effective strategies is essential for successfully managing this autoimmune condition and minimizing its effects on daily activities.
Contents
- 1 Living with Psoriatic Arthritis: Daily Challenges and Solutions
- 2 Signs and Symptoms of Psoriatic Arthritis
- 3 Implementing Lifestyle Changes for Better PsA Management
- 4 Navigating the Medical Landscape: From Diagnosis to Treatment
- 5 Potential Side Effects of NSAIDS
- 6 Emerging Treatments
- 7 Holistic Approaches to Psoriatic Arthritis Management
- 8 Best Foods for Managing Psoriatic Arthritis
- 9 Author
Living with Psoriatic Arthritis: Daily Challenges and Solutions
PsA can affect various aspects of daily life, from simple tasks to work responsibilities. Joint pain, stiffness, and fatigue can make routine activities challenging. Many individuals with PsA report difficulty with tasks such as getting dressed, preparing meals, or even typing on a keyboard. To navigate these challenges, it’s essential to develop coping strategies. Using assistive devices, such as jar openers or ergonomic keyboard, can help reduce joint strain. Planning rest periods throughout the day and prioritizing tasks can help manage fatigue.
Signs and Symptoms of Psoriatic Arthritis
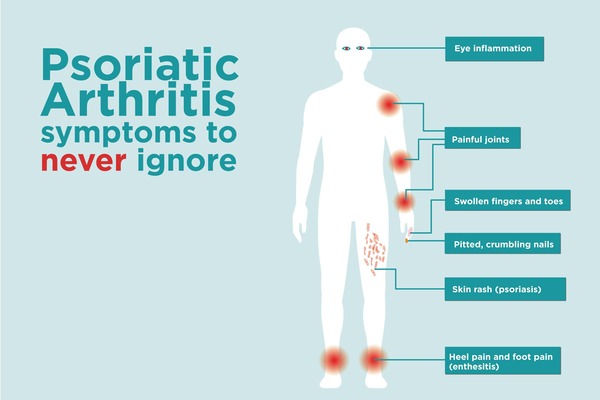
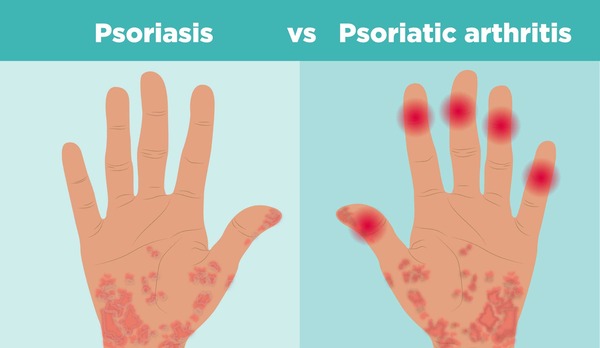
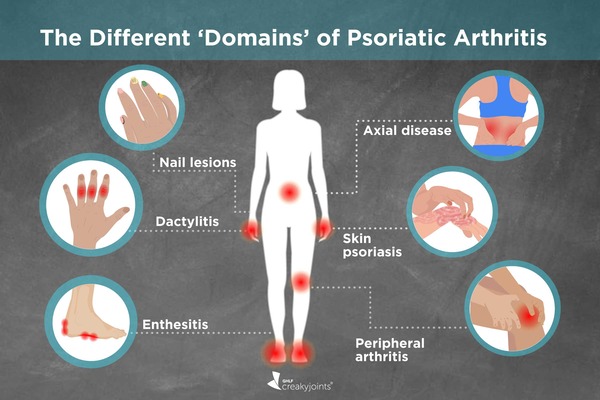
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is characterized by a range of signs and symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. The primary symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, which can affect any joint in the body. Individuals with PsA often experience skin rashes typical of psoriasis, presenting as red, scaly patches. Fatigue is a frequent complaint among those with PsA, along with tenderness where tendons and ligaments attach to bones, known as enthesitis. Symptoms can vary widely from person to person, with some experiencing mild discomfort and others facing severe, debilitating pain. Skin symptoms often precede joint symptoms.
Implementing Lifestyle Changes for Better PsA Management
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in psoriatic arthritis management and improving overall health. One of the most impactful changes is maintaining a healthy weight. Excess weight puts additional stress on joints, exacerbating pain and inflammation. A balanced, anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and support joint health. Regular exercise is another vital component of PsA management. Low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, or yoga can maintain joint flexibility, strengthen muscles and improve overall fitness without putting excessive stress on joints. Learn more about Ritual Multi Vegan Supplements.
When symptoms of PsA first appear, begin by consulting your general practitioner or primary care physician. One may then be referred to a rheumatologist, a specialist in musculoskeletal diseases and systemic autoimmune conditions. Rheumatologists play a central role in diagnosing and treating PsA. In some cases, dermatologists may also be involved, especially if skin symptoms are prominent. The first line of defense against PsA may involve non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) to manage pain and inflammation. Transform your Health with Orga Organic.
Potential Side Effects of NSAIDS
While NSAIDs are effective in managing pan and inflammation associated in psoriatic arthritis, they can have potential side effects. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as stomach pain, ulcers, and bleeding. Long-term use of NSAIDs can also increase the risk of cardiovascular problems, including heart attacks and strokes. See Osprey Lifestyle gear for hiking, biking and travel.
Emerging Treatments
The field of PsA treatment is continuously evolving, with new therapies offering hopes for better symptom management and disease control. Biologic medications, which target specific components of the immune system, have revolutionized PsA treatment in recent years. These drugs can be highly effective in reducing inflammation and preventing joint damage. Classes of medications such as Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors work by blocking specific pathways involved in inflammation. The FDA revised its recommendations recently; JAK inhibitors should be avoided in people over 65 years old, current and former smokers, and anyone with risk factors for heart disease or cancer.
Holistic Approaches to Psoriatic Arthritis Management
While medical treatments form the cornerstone of PsA management, holistic approaches can complement traditional therapies. Acupuncture has shown potential in reducing pain and improving function in some individuals with PsA. Massage therapy can help alleviate muscle tension and improve circulation, potentially easing joint stiffness. It’s important to discuss any complementary therapies with your healthcare provider to ensure that they’re safe and appropriate.
Best Foods for Managing Psoriatic Arthritis
Diet plays a significant role in psoriatic arthritis management. Consuming anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce flare-ups and improve overall health. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, mackerel and walnuts, are particularly beneficial for reducing joint inflammation. Antioxidants-rich fruits and vegetables, like berries, spinach, and kale, can also help combat oxidative stress caused by chronic inflammation. Whole grains, such as brown rice, and quinoia are excellent sources of fiber and can help maintain a healthy weight, which is crucial for PsA management.
Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and fermented vegetables can promote gut health, which is often compromised in individuals with PsA. Conversely, try to avoid foods that trigger inflammation, such as red meat, processed foods, and sugary snacks. These foods can exacerbate symptoms and contribute to weight gain, further stressing the joints.
By combining medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and a proactive approach to self-care, individuals with PsA can effectively manage their condition and maintain a fulfilling, active life. As always, this paper is for information purposes only. If you suspect that you has PsA, consult with your general care physician for proper evaluation and personalized treatment.
Barry Schustermann
Follow me on X @BarrySchust
Follow me on Facebook @Barry Schustermann
External References:
- Arthritis Foundation: https://www.arthritis.org/diseases/psoriatic-arthritis
- National Psoriasis Foundation: https://www.psoriasis.org/about-psoriatic-arthritis/
- American College of Rheumatology: https://www.rheumatology.org/I-Am-A/Patient-Caregiver/Diseases-Conditions/Psoriatic-Arthritis
- Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/psoriatic-arthritis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20354081
- Creaky Joints: https://creakyjoints.org/education/psoriatic-arthritis/



1 thought on “Psoriatic Arthritis: A Guide to Management and Treatment”
Comments are closed.